As I previously mentioned I would like to launch a second blog featuring small facts or insights that are widely disbelieved despite being known to be true by the experts in the relevant field or facts that are very surprising or misunderstood by a lot of people. These facts shouldn’t be trivia but important facts that are somewhat easy to understand despite their status as being unthinkable to many. They are not scientific theories or complex sets of facts or information, but facts that you can easily state. They may be part of a scientific theory, or a result of an established scientific theory but not an entire scientific theory. I’ve collected hundreds of these facts because to me they seem to be extraordinarily important. They are worldview altering facts, big shocking facts to some, facts that many people deny regardless of the evidence, super-facts if you will.
In a previous post I discussed that despite the fact that the scientific community states that Earth is 4.5 billion years old and that humans evolved over millions of years a 2019 Gallup poll, showed that 40% of US adults believe that God created humans in their current form within the last 10,000 years. The evidence proves that this 40% of the population is wrong. The scientists aren’t guessing. They make their claim that earth is 4.5 billion years old based on a lot of strong evidence. Evidence which is unknown to a lot of people. In this post I am discussing a fact that once was widely disputed but today is more just surprising or not understood by many and that is that the speed of light in vacuum is a universal constant.
No matter how fast you travel, what direction, or where you are you will measure the speed of light compared to yourself to be c = 299,792,458 meters per second or approximately 186,000 miles per second or 671 million miles per hour.
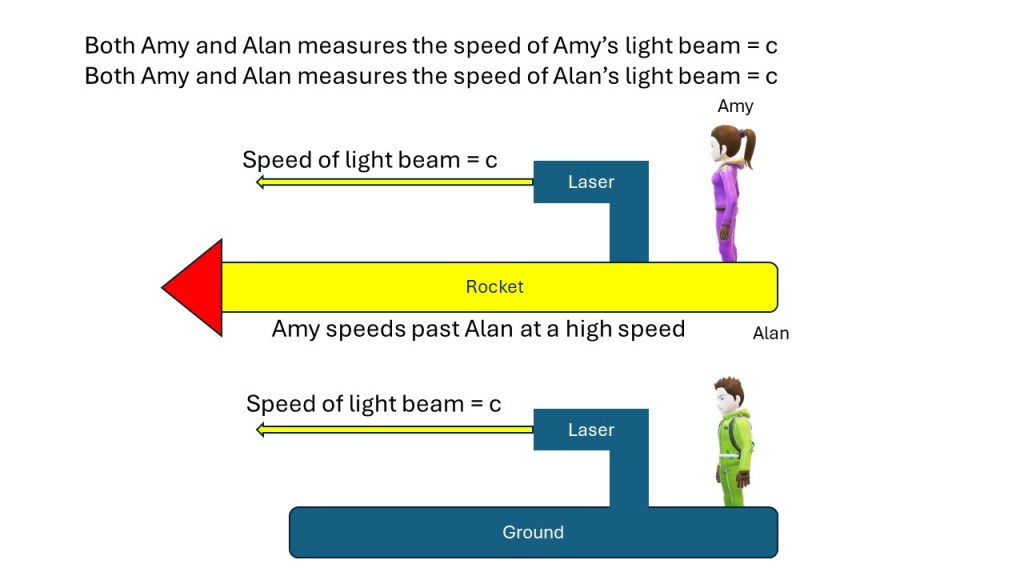
In the picture above let’s say Amy is flying past Alan at half the speed of light. If you believe Alan when he says that both laser beams are traveling at the speed of c = 186,000 miles per second, then you would expect Amy to measure her laser beam to travel at a speed that is half of that c/2 = 93,000 miles per hour, but she doesn’t. She measures her laser light beam to travel at the speed of c = 186,000 miles per second just like Alan. This seems contradictory. The solution that the special theory of relativity offers for this paradox is that time and space are relative and Amy and Alan measure time and space differently (more on that in another post).

I should add that the realization that the speed of light in vacuum is a constant regardless of the speed or direction of the observer or the light source was a result of many experiments, which began with the Michelson-Morley experiments at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio in the years 1881-1887. At first scientists thought that there was an ether that compressed the experimental equipment and distorted clocks so that it seemed like the light vacuum always came out the same. With the special theory of relativity in 1905 those speculations were laid to rest.
The speed c = 299,792,458 meters per second is a universal speed limit created by time and space
I should point out that there is nothing magical about the speed of light in a vacuum. Light traveling through matter, like glass or water, does not travel at this speed c, but slower. It also isn’t entirely correct to say that the speed of light in vacuum is a universal constant, because it isn’t about light per se. What is happening is that light traveling completely unimpeded through vacuum is prevented from traveling infinitely fast by the way time and space is set up. All massless particles / radiation, or anything that hypothetically could be traveling at an infinite speed is prevented from doing that because of the way time and space are related. Light in vacuum just happened to be what we first discovered to be restricted by this universal speed limit. Yes, time and space are annoying that way, putting a limit on the speed of light and on massless particles.
So how is time and space arranged to cause this universal speed limit? Well, that is an even more surprising blog post for another day (I will link to it once I have made the post). From this discovery about time and space came a lot of other interesting realizations but that is also for another post, but let’s just give a brief summary:
- Time for travelers moving fast compared to you is running slower.
- Length intervals for travelers moving fast compared to you are contracted.
- Simultaneous events may not be simultaneous for another observer.
- The order of events may be reversed for different observers.
- If you accelerate to a speed that is 99.999% of the speed of light you still haven’t gotten any closer to the speed of light from your perspective. Light in vacuum will still speed off from you at c = 186,000 miles per second.
- Acceleration will get harder the closer you get to the speed of light in vacuum. The force required will reach infinity as you approach the speed of light in vacuum.
- Forces, the mass of objects, momentum, energy and many other physical quantities will reach infinity as you approach the speed of light in vacuum assuming you are not a massless particle.
- Mass is energy and vice versa E = mc2
- Magnetic fields pop out as a relativistic side-effect of moving charges.

How do you feel about time and space creating this universal speed limit in which light in vacuum travel?





