What is the greatest intellectual achievement of the human race? Is it Beethoven’s third symphony? The book War and Peace by Leo Tolstoy? General Relativity? Quantum Physics? multi layered neural networks? Or is it a theory of almost everything that comprises quantum physics, special relativity, Noether’s theorem and gauge theories, as its basic elements, and then Quantum Electrodynamics, Quantum Chromodynamics, and a framework for all elementary particles, and more. This is the so called “standard model of elementary particles”, or the “standard model” for short. It is a subjective question.

Some people like to say, “Science does not know everything”. They are right. If it did, it would stop. However, the people who like to say that typically grossly underestimate what science knows, and not by a little but by a lot, like a million times, or a trillion times. There are things science knows and there are things it doesn’t know, and the difference is often not obvious unless you have near expert knowledge. However, we have figured out a lot. The book I am describing below is a breathtaking reminder of how much we know. It is the book about the theory of almost everything after all.

I read The Theory of Almost Everything: The Standard Model, the Unsung Triumph of Modern Physics Hardcover – July 22, 2005, by Robert Oerter, more than 15 years ago. I wrote a lengthy review, which is still the top review for this book. The hardback version is 336 pages. It currently costs $31.93. The dimensions of the hardback are 6.5 x 1.25 x 9.75 inches, and the weight is 1.2 pounds, ISBN 978-0132366786. The paperback version is 336 pages. It currently costs $17.00. The dimensions of the paperback are 5.5 x 0.8 x 8.4 inches, and the weight is 10.9 ounces, ISBN 978-0452287860. The kindle version costs $13.99 and is 348 pages ASIN : B002LLCHV6.

Someone reminded me that today, Wednesday August 9, is National Book Lovers Day. Even though I already published a post on a Leonberger book today I decided to post about one more book, one of the most mind-blowing books that I’ve ever read. I have a master’s in engineering physics from Uppsala University that was turned into a master’s in electrical engineering and applied physics by Case Western Reserve University in Ohio. That is why I am interested in this topic, which I understand is not everyone’s cup of tea, maybe no one’s. I took a few classes in Quantum Physics, Nuclear Physics, and Molecular Physics, and I had heard of the standard model, I just never realized what it was. Then I read this book many years later and as I said, I was blown away.
Quick note, if you have never heard of Noether’s theorem, don’t worry, almost no one has, yet it is an extremely important discovery in mathematics. Emily Noether discovered that associated with every symmetry was a conservation law and vice versa. It is one of the greatest discoveries of mankind, yet almost no one has heard of it. For example, if you assume (rather acknowledge) that the laws of physics don’t change over time, then energy is conserved. If you acknowledge that the laws of physics don’t change as you change position, then momentum is preserved. You use mathematics to derive one from the other. This is very useful because, if you find a symmetry you can find a conservation law. If you find a conservation law, you can find a symmetry. This has turbo charged modern physics.
The standard model does not get a lot of love. One reason is that unless you have a physics education it is difficult to grasp. It is also a gigantic theory. Well actually not really. You can summarize it in a few formulas that almost no one can understand, as the author of the book does. Another reason is that as soon as physicists were done with it, they were looking to replace it. That was because of the “Almost” in “the theory of almost everything”. There were a few things it could not explain, and it was not compatible with General Relativity even though it incorporated Special Relativity. Anyway, I cleaned up my review a bit and it is given below. If you want to see my original Amazon review, click here.
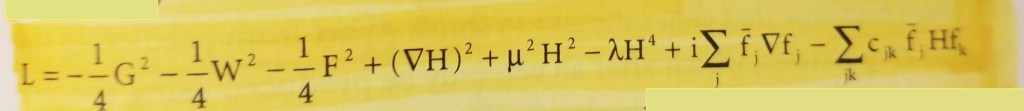
Note; when I wrote the review below, we had not yet found the Higgs Boson. It was found at LHC in Switzerland in 2012.
An introduction to the greatest intellectual achievement of the human race
This review is a little bit long; however, it is more than an assessment of the book, it will also help you prepare for reading the book and explain confusing parts of the book.
Imagine if we had found a two-billion-year-old alien underground civilization under the desert in Arizona several years ago, and you still knew nothing about it, because journalists thought this information was pretty boring stuff and therefore didn’t bother telling anyone about it. Well, that is most likely not true, but what is true is that the general public has entirely missed the greatest scientific revolution in the history of the human race partially because mainstream media has largely ignored this information, even though the Nobel Prize committee has been raining Nobel Prizes over it.
In the 70’s a theory explained, at the deepest level, nearly all of the phenomena that rule our daily lives came into existence. The theory called “The Standard Model of Elementary Particles” is a set of “Relativistic Quantum Field Theories” that explains how elementary particles behave, which elementary particles there are, and why they have the properties they have, for example, isospin, spin, charge, color charge, flavor, even mass, or mass relations in many cases. The theory explains how all of the fundamental forces in nature work except gravity. The theory describes how the elementary particles interact; decay, how long they are expected to exist, and how they combine into other subatomic particles. The theory uses only 18 adjustable parameters to accomplish this.
In the extension the theory thus explains how nucleons and atoms are formed and what properties the atoms will have, and how molecules will form and what properties molecules will have, their chemical reactions, and what elasticity, electric conductivity, heat conductivity, color, hardness, texture, etc. any material will possess. In the extension it explains why mass and matter exist, how the sun and the stars work, and the theory is therefore the ultimate basis of all other science. It also provides a formula, or an equation of almost everything. Best of all it has been thoroughly verified experimentally, in fact the predictions the theory has made have been confirmed with such stunning accuracy and precision that it could be considered the most successful scientific theory ever. A theory that successfully unites all of physics and basically all of human knowledge of the Universe into one single theory has never before existed.
However, “The Standard Model” does not incorporate gravity and the general theory of relativity, and cannot explain dark energy, dark matter and why neutrinos have mass. Therefore as soon as the theory came into existence physicists started looking for the next theory that would finish what the “The Standard Model” did not finish. Example of such theories are GUT theories, SO(5), SO(10), string theories (abandoned), super string theories, and M-theories. Even though those new theories are extremely interesting they have not been verified or able to predict anything. In comparison with the “Standard Model”; superstring theories, grand unified theories, chaos theories, you name it, are essentially nothing, but are still better known.
This book explains to the layman what the “Standard Model” is and how it came into existence. The book is by no means a perfect book. I think there are several problems with the book. However, I decided not to take off any star because there are very few books written for science interested non-physicists that explain the “Standard Model of Elementary Particles”. Dr. Oerter deserves five stars just for his fairly decent attempt at doing so.
Even though the book is a Physics book, it is also a book on Philosophy. In fact Physics is often the best and the deepest Philosophy, the kind of Philosophy that can be falsified, verified and proven wrong or correct. To understand what I mean consider Noether’s theorem. Noether’s theorem states that whenever a theory is invariant under a continuous symmetry, there will be a conserved quantity. As an example of what a continuous symmetry is the following: any physical experiment that is performed at a certain time will have the same result if it is performed exactly the same way a certain time later. That seemingly self-evident observation means that Energy is conserved. Another example is, any physical experiment that is performed at a certain place will have the same result if it is performed exactly the same way somewhere else. That seemingly self-evident observation means that momentum is conserved.
Let me add that “exactly the same way” really means that! Gravity, other forces, differences in light, or anything else cannot be different in the second experiment. The only thing allowed to be different is the position “x” (if that is our symmetry variable). That is what continuous symmetry means, changing just one thing, and everything stays the same.
Noether’s theorem has been the guiding principle behind the standard model, and it is used to find conservation laws where symmetries are found, and it is used to find symmetries where conservation laws are found. It is a spontaneous symmetry brake that allows the Higgs Boson to give all other particles their mass (excepting mass less particles). This is why matter and everything in our Universe exist. The Higgs Boson is also called the God particle (guess why). So Noether’s theorem is both very useful in a practical sense and deeply philosophical at the same time.
The God particle has not yet been found, but scientists will be looking for it using the new Large Hadron Collider (LHC) that will come on line this fall (fall of 2008). LHC will start operating in August and the first collisions are planned for October. It is the largest machine ever built and it has a circumference of 17 miles. However, a lawsuit has been filed in an attempt to stop the LHC from operating. Some people believe that the LHC will create small black holes that could suck up all of the earth. In essence, they believe that our attempt to find the God particle will be the end of the world.
In addition to Noether’s theorem the standard model is built upon the special theory of relativity and a modern formulation of quantum mechanics (Quantum field theory), QED, QCD, as well as some discoveries regarding elementary particles. I can add that Noether’s theorem was formulated by a Jewish woman, Emmily Noether, who could not get a job in academia because she was a woman. This theorem is one of those very important but mostly unknown discoveries, like the invention of paper by the Chinese Tsai Lun.
Oerter does not attempt to explain the special theory of relativity; however, he tries to give the reader an idea of what it is. The problem with his approach is that he gives the reader just enough information to enable the observant reader to come up with the apparent paradoxes within the special theory of relativity, but not enough information to help the reader to easily resolve them.
He also confuses the reader by not distinguishing between rest mass and relativistic mass. The observant reader will think that he is contradicting himself. The term relativistic mass is the total mass and the total quantity of energy in a body. The rest mass is the mass of a body when it is not moving. The formula E = mc² is always true, when it refers to relativistic mass, which is why we talk about an energy/mass equivalence. The other more complex formula Oerter presents refers to rest mass. There is no such thing as an energy/rest mass equivalence (except at speed 0) but that is what the reader who is not already familiar with the subject will end up believing.
Another mistake Oerter makes is in regard to the fact that the speed of clocks will be measured differently in different reference frames. On page 35 last paragraph Oerter writes “Here, we have an apparent paradox: If each reference frame sees the other as slowed down, whose clock will be ahead when the passengers leave the train?” Then he implies that the paradox has to be solved by incorporating the General theory of relativity. Even though that may be how it was first solved, you can solve this form of the so called “Twin Paradox” and other similar paradoxes from within the framework of the special theory of relativity itself.
Oerter explains Quantum Physics in a very typical manner, but he mostly avoids making it look much weirder than it actually is which he should be commended for. However, there is one thing that all Physicists seem to do when they explain Quantum Physics to the layman which annoys me greatly. The matter waves (or quantum fields) in Quantum Physics are quite strange entities. The reason they are so strange is because they do not exist in a real sense, they are more correctly stated mathematical abstractions. Oerter states this clearly, which is good. However, he then goes on to mention De Witts’ idea about multiple Universes without acknowledging that these “bizarre solutions” to Quantum Wave conundrums are completely unnecessary and worthless. There is no more reason to believe in multiple Universes based on matter waves than there is to believe in multiple Universes because we all have different reference frames.
In fact when I took my first class in Quantum Physics (as an engineering physics student) I successfully proved, using a combination of the Schrödinger equation and plain Galileo transformations, that the matter waves are not only “not real” they don’t even represent information in an objective sense, in fact every reference frame had its own matter wave for the same particle. Our own single Universe is thus already all the Universes you need all at once. My associate professor was just scratching his head but the leading Swedish authority on Quantum Physics at the time, Staffan Yngwe, immediately agreed with me. So, in summary there is no need to make Quantum waves weirder than they are or draw unwarranted conclusions from apparent conundrums. Just take them for what they are; one possible mathematical model (among many) of a particle as seen from your frame of reference only.
After giving a background to the special theory of relativity and Quantum Physics Oerter continues explaining relativistic Quantum Physics including the fantastic prediction you get when you combine the special theory of relativity with Quantum Physics; that for every particle there is a twin particle with exactly the same mass, and spin, but opposite charge and isospin. These particles were called anti-particles and until they were actually found physicists tried to get rid of them from the theory. However, the combination of the special theory of relativity and Quantum Physics would lead not only to much better explanation for such things as the radiation and light spectrum and the properties of atoms, it would also lead to new discoveries.
Richard Feyman came up with a new representation of relativistic quantum physics for electrons that did not use waves called Quantum Electro Dynamics, and this was one of the first steps towards the standard model. Physicists started discovering a lot of unexpected particles which remained unexplained for decades (until the standard model came about), QCD was invented, the Higgs Boson (the God particle), symmetry breaks, etc. The story is simply breath taking and Oerter does a good job telling this story, except I think he should have used more and better pictures. However, as I said I cannot honestly take any stars off for these minor flaws. Finally Oerter discusses possible modifications to the standard model, GUT’s, string theory (abandoned), super string theories, and M-theories.
I also would like to add an interesting fact that I think everyone should be aware of. There are elementary particles with whole number spin and they are called Boson’s, and there are elementary particles with half number spin called Fermions. The Pauli Exclusion Principle (that no two particles can occupy the same state) applies to Fermions but not Bosons and therefore the two different types of particles behave very differently and follow different kinds of statistical rules (Bose-Einstein statistics versus Fermi-Dirac statistics). All force carriers are Boson’s while some Fermions are used to build “nomral matter”. Examples of Bosons are the photon, gluons, W and Z Boson, mesons, the Higgs Boson (the God particle). The Fermions come in three families each with four particles and their anti particle.
Electron / positron
Neutrino / anti-neutrino
Up quark / anti up quark
Down quark / anti down quark
muon / anti-muon
Mu Neutrino / anti-mu-neutrino
Charm quark / anti charm quark
Strange quark / anti strange quark
tau / anti-tau
Tau Neutrino / anti-tau-neutrino
Top quark / anti top quark
Bottom quark / anti bottom quark
The quarks can be used to build other particles. For example, a quark and anti-quark pair is called a meson (there are many kinds of mesons). A triplet of quarks is called a Baryon. An example of a baryon is the proton which consists of two up quarks and one down quark. Another example is the neutron which consists of one up quark and two down quarks.
I highly recommend this book for anyone who wants to understand something about our world and the Universe. However, don’t expect to understand everything, it is not written so that you can. I wish Physicists would become a little better at explaining these things to the layman using nice descriptive pictures and a little bit of math too (don’t assume math is always bad). I once read a 30 page long Swedish book on the special theory of relativity that successfully explained the kinematics, dynamics, and magnetism in relativity, to your average high school kid. The Lorenz transforms, formulas for acceleration, E = mc², and magnetism were derived using simple algebra and a tiny bit of calculus at one point. That is the way these kinds of books should be written, but I have seen this only once in my life. Excluding this single example (Swedish book), Oerter’s book is one of the best books on Physics for the layman that I have ever read.
Finally, I would like to ask a question for discussion. Will you and our planet survive this coming fall considering that the LHC is coming online?


Ooh this sounds like a great book! I’m genuinely interested. I read a book by Stephen Hawking about grand design and he touched on those topics. I found it fairly easy to follow which is a sign of genius – simplifying things so most people can understand.
I couldn’t finish the book since one of my parents ripped it off and probably threw it away (they were against secular science).
Your book review reminds me of this cool topic. Thanks for sharing! I may read it.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thank you Sara. I read the grand design too. It was a great book like this one. Actually this one is a little easier to follow than the grand design, I think. If you liked the grand design you might like this one too. I can’t believe your parents ripped it off and threw away the book.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Yeah 😦 but I’ll buy it again! And also check yours out!
LikeLiked by 2 people
That sounds great. Thank you Sara.
LikeLiked by 1 person
The beginning of Time by Hawking is great one
LikeLiked by 2 people
Ooh I’d love to check it out ! 😊
LikeLiked by 2 people
I will be happy if you read my post on Cosmology
Regards 🙏
LikeLiked by 2 people
Sure I’ll check it out 😀
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thank you 🙏
LikeLiked by 2 people
HI Thomas, this does sound like an interesting book for people who enjoy delving into science. My son, Greg, might like this. I will ask him. I have always thought that the wheel was the most important scientific invention ever made.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Yes Greg might like it. Maybe he read one of Stephen Hawking’s books? Then he is likely to like it. About the wheel, yes maybe, it is a subjective question. No one knows who invented the wheel though.
LikeLiked by 2 people
HI Thomas, yes, Greg did read Stephen Hawking’s books and he also did physics and chemistry to his final year to high school. He isn’t pursuing science at Uni although he is doing a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science. He now wants to do a quadruple major over two years so he will have majors in mathematics and computer science. Greg is very clever, he gets in the 90s for many of his Uni subjects.
LikeLiked by 3 people
Wow that is very impressive! 🥇🏆and those are great fields. Congratulations to Greg and to the whole family.
LikeLiked by 2 people
🥰💕
LikeLiked by 1 person
You read like I did in my early 30s before I became a professional writer.
How many books do you read per week?
I used to average 1 to 2 books per week. Now that I’m writing regularly, it takes half a month to get through a book.
This sounds like something I’d love to read. Another one for the “pile.”
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you MaryAnne. It was your reminder of the National Book Lovers Day that inspired me to make two book posts in one day. I read about one book per week, but here I only post Leonberger books and books I want to promote, which is just a subset of what I read. I would like to start a second blog and post non-Leonberger stuff there and stop doing that here. I also would like to start using other people’s Leonbergers to post here because it looks like it’s going to be a while before we get another Leonberger. I will ask Leonberger folks.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Sounds like a great plan!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you MaryAnne
LikeLiked by 1 person
An excellent selection for National Book Lovers Day. Going on my TBR.
LikeLiked by 1 person
That is great. Thank you so much Priscilla.
LikeLiked by 1 person
This sounds fascinating, Thomas. I like your review very much.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thank you for your kind words Kymber.
LikeLiked by 1 person
You are so far over my head, I didn’t even feel the breeze. Hmmm…
LikeLiked by 2 people
LOL. We all have different interests. If you are still interested in those topics I think Neal De Grass Tyson’s books are more accessible. Both Hawking and Oerter are somewhat challenging.
LikeLiked by 2 people
I was going to say essentially the same thing, but could never have done so as brilliantly as Jacqui did!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Yes it was a creative way of putting it. I like these topics but it is not everyone’s cup of tea. However, the books by Neil De Grasse Tyson are more accessible.
LikeLiked by 1 person
I probably wouldn’t get past the titles. 😛
LikeLiked by 1 person
Hehee
LikeLiked by 1 person
Astrophysics for People in a Hurry by Neil De Grasse Tyson Maybe?
LikeLiked by 2 people
Ha! That’s a great title. 🙂
LikeLiked by 2 people
It’s been a long time since I’ve read anything on physics. I’m not a physicist (what gave it away?), but I was intensely interested when I was younger. I read Hawking, Feynman, and a number of others. I even read Einstein’s work on the Theory of Relativity. I had to dedicate a couple of afternoons to that. This might be a nice refresher.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Yes I think this might be a book for you. The standard model is based on Feyman’s way of expressing Quantum Physics and the standard model is a compact summary of most of modern physics. This book explain the special relativity and could be a good refresher, except I’ve seen better explanations of relativity. But it would be a good refresher on Feynman, Quantum Physics, the fundamental forces and elementary particles.
LikeLiked by 1 person
thanks, Thomas. Though I may have to reincarnate to read it. 🙂
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks for sharing this idea of this book.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Anita
LikeLike
This stuff fascinates me for a few minutes, then I start to get lost but push a little further to exercise my brain. Thanks for suggesting Neal De Grass Tyson’s books in your comments above. I hope human ethics and compassion catch up with our intellectual achievements.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Yes that is an important point you are making. I hope so too.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Nice review, Thomas!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Alex
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thanks for the recommendation.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you for visiting and commenting Rosaliene
LikeLiked by 1 person
Wow! Thomas, this is one of the most academic yet passionate reviews I have ever read. Not something I would reach for but I’m forwarding this to my son who might very well be interested!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Annika for your very kind words. That’s sounds like a great plan. If he is interested in this topic I hope he likes it.
LikeLiked by 1 person
He’s just graduated university in software engineering and AI but studied physics and maths to A-level standard and got top marks and is indeed interested in topics such as this!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Wow that is so impressive. Your son would certainly not have any problems understanding this book and yes it sounds like he would be interested in this book. Annika congratulations to your son 🥇🏆🥂
LikeLiked by 1 person
hello, thank you for stopping by! have a nice day!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Carfax have a nice day you too
LikeLiked by 1 person
That was an amazing review, Thomas. Most of it was over my head (I’d have to start with something much more basic), but I do find science fascinating … and philosophical/spiritual. My mother used to say that if you traveled far enough West, you’d end up in the East, and I see evidence of that all the time. I read The Dancing Wu Li Masters decades ago and my fascination with Quantum Physics has continued since. You’ve piqued my interest. Thanks for sharing your review and a bit of your remarkable experience and knowledge.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you so much for your kind comment Diana. I am certainly interested in Quantum Physics as well. I took a few university classes, and I’ve read a lot of books since then. I am especially interested in the interpretation of things like superposition of waves and the double slit experiment. I read the book you mentioned but a very long time ago. I recently read a book called “What is Real” and is currently reading “Beyond Weird Beyond Weird” by Philip Ball. The latter is another five star book.
LikeLiked by 1 person
🙂 😀 I love how clearly enjoy this stuff.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Diana
LikeLiked by 1 person
Physics was not a strong suit back in school for me, but over time, I grew to want to know more. I totally believe in quantum physics and bringing the forces into your being for the usage of good.
LikeLiked by 1 person
That sounds great. Thank you for commenting Ray.
LikeLike