It is very common for veterinarians, ASPCA and other animal welfare organizations to recommend that dogs be neutered or spayed between the ages 6-9 months or earlier. Their concern is chiefly to prevent unexpected pregnancies, which causes a lot of suffering and unnecessary euthanasia of dogs. However, not all dogs are the same and this is bad advice for many giant breeds, especially Leonbergers. Neutering or spaying too early can lead to serious health complications. Since the Leonberger community tries to prevent irresponsible dog owners from getting a Leonberger, unexpected pregnancies are less of a concern for Leonberger dogs.
We used to own a Leonberger dog, Le Bronco von der Löwenhöhle, and our breeder recommended that we wait until he was at least two years old before neutering him. Many new Leonberger owners must sign a contract promising not to neuter the dog before the age of two. If you want to buy a Leonberger puppy in North America, you should buy the puppy from a breeder that is certified by the Leonberger Club of America (LCA) and to do that you need to go through an interview. You will have a hard time getting a Leonberger any other way.

I should explain that the Leonberger is a rare breed that is closely related to the Saint Bernard. Saint Bernards were used to create the Leonberger in the early 19th century and later it was the other way around when the Leonberger was used to save the Saint Bernard breed. Therefore, Leonbergers and Saint Bernards are genetically similar, they are about the same size, but they don’t look the same. Leonbergers have a characteristic black face while Saint Bernards have a white mask on their face. There are only about 30,000 Leonbergers in the world and only 2,000 Leonbergers in North America. Therefore, the Leonberger community is a small and tightknit community, and it is relatively easy for the Leonberger Club of America (LCA) to keep track of what is going on with the Leonberger dogs.

With this post I am giving advice and statements originating from various sources that I consider to be reputable such as AKC/club certified breeders of the specific breed in question, the corresponding breed organization/club, such as the Leonberger Club of America, and scientists in the specific field. In my experience veterinarians who care for all kinds of dogs and pets typically do not have knowledge that is breed specific on this issue. To be sure to do the right thing in regard to neutering and spaying your Leonberger, ask your LCA certified breeder.
What Our Leonberger Breeder Told Us About Neutering
When we got our late Leonberger Bronco (Le Bronco von der Löwenhöhle) our breeder Julie Schaffert told us to wait with neutering him until he was two years old if possible. Julie Schaffert has been an LCA (Leonberger Club of America) certified breeder since 1992 and is arguably the most prominent Leonberger breeder in North America. After reading a Leonberger book that incorrectly stated that Leonbergers should be neutered at six months, I sent her this question:
Hello Julie, I hope all is well with you and your Leonbergers. I am currently reading a Leonberger book by Vanessa Ritchie. I’ve read dozens of Leonberger books. It is a very good Leonberger book. However, in the middle of page 30 she is saying something that concerned me. She is saying to neuter/spay your Leonberger at 6 months old. I remember you telling us to wait with ours and we waited until significantly passed one years old. Assuming that is correct, this mistake needs to be pointed out and perhaps corrected. Before saying anything, I wanted to make sure that is correct, that spaying/neutering at 6 months old is indeed too early for a Leonberger.
Thank you for any help
Happy New Years
Thomas Wikman
This was her answer
Happy new year. Yes, it’s now recommended that giant dogs not be neutered or spayed until after 2 years. In the old days it was recommended earlier, any time after 6 months. All the new data says wait.
Julie.

The reasons we did not wait the entire two years was that our veterinarian at the time wanted to do it sooner and Bronco was dragging furniture around the house because of his excess energy. He was strong, and big, energetic and a bit restless. He was very friendly and harmless, but he had a lot of energy. Perhaps he should have been a home decorator? I should say that knowing what we know now, we would have waited the entire two years.

Research and Expert Advice on Neutering and Spaying
This is an article from the AKC stating that a larger or giant breed may need to wait until they are near or over 12-18 months of age before neutering or spaying. The article also provides the following interesting information.
Research conducted by the University of California – Davis reveals that for some dog breeds, neutering and spaying may be associated with the increased risks of certain health conditions such as joint disorders including hip or elbow dysplasia, cranial cruciate rupture or tear, and some cancers, such as lymphoma, mast cell tumor, hemangiosarcoma, and osteosarcoma. The research conclusions are not surprising. Sex hormones are important in the development of any animal. We know they affect psychological development as well as the musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, and the immune system.
I believe this is the University of California – Davis article in question. It is from 2020. Notice that the suggested guidelines for age of neutering is beyond 23 months for several of the giant breeds in the table of 35 breeds. Also notice that the table does not include Leonbergers.
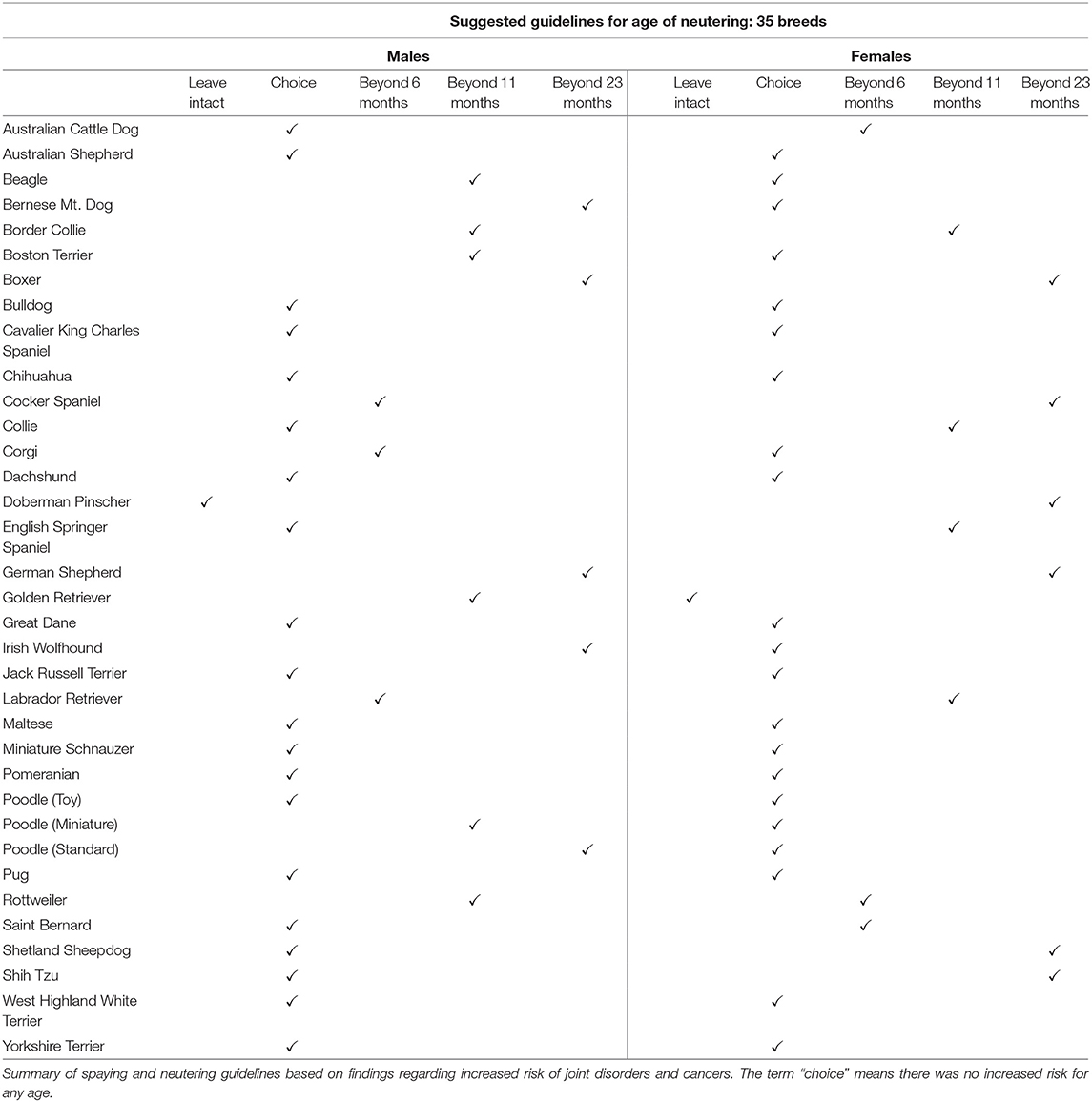
Recommended ages for neutering and spaying for selected dog breeds
Below is a list featuring the recommended ages for neutering and spaying for selected dog breeds based on the research mentioned above.
- Australian Shepherd, for neutering and spaying it is your choice. The same is true for Pugs.
- Bernese Mountain Dog, you should neuter beyond the age of 23 months, but for spaying you have a free choice.
- Boxer, neuter and spay beyond the age of 23 months.
- Boston Terrier, neuter beyond 11 months, but for spaying you have a free choice.
- Doberman Pincher, never neuter, and you need to spay beyond the age of 23 months.
- German Shepherd, neuter and spay beyond the age of 23 months.
- Labrador Retriever, neuter beyond 6 months and spay beyond 11 months.
- Corgi, neuter beyond 6 months, but for spaying you have a free choice.
- Great Dane, despite being a very large dog you have a free choice for both neutering and spaying.
- Rottweiler, neuter beyond 11 months, but for spaying beyond 6 months.


Additional Information on Neutering and Spaying Various Dog Breeds
Hillhaven Leonbergers in Ireland recommend not neutering your Leonberger until at least 2 years of age. They warn against doing it at 6 months old, despite what some veterinarians may recommend.
I did not find an on-line Leonberger Club of America recommendation but this old 2011 article from the Leonberger Club of America states: Because the Leonberger is a slow maturing breed in general, most breeders will ask puppy owners to wait a year or so before altering their puppies, to allow bones to develop more fully.

I did find an article from the Saint Bernard Club of America. The Saint Bernard is genetically similar to the Leonberger. This article states: Above all, no giant breed puppy should be altered before the growth plates in the bones have matured and closed, usually between 15 and 24 months of age.

This Newfoundland dog magazine states : Currently, the recommended age that a Newfoundland dog should be neutered is 18 to 24 months due to the possible health problems that can arise from altering before that age. The Newfoundland is another dog that is genetically similar to the Leonberger.

Conclusion
So, in conclusion, even though the expert advice regarding neutering and spaying varies a bit, it is clear that neutering and spaying at six months old is too early for Leonbergers and many other giant breeds. It can harm their Leonberger.
About Thomas Wikman
Thomas Wikman is a retired software / robotics engineer with a background in physics. He has a PhD in Applied Physics and Electrical Engineering. He is the author of two blogs, first this blog Leonberger Life which is focused on a rare but amazing dog breed called Leonberger. He has also written a book titled The Life and Times of Le Bronco von der Löwenhöhle, which feature his Leonberger’s crazy adventures as well as information about the Leonberger breed and how to care for giant dog breeds. His second blog superfactful , is a fun but educational blog that is focused on finding facts that are important and yet surprising or disputed by people who are not well informed on the topic. This blog features myth busting as well as facts that will blow your mind.