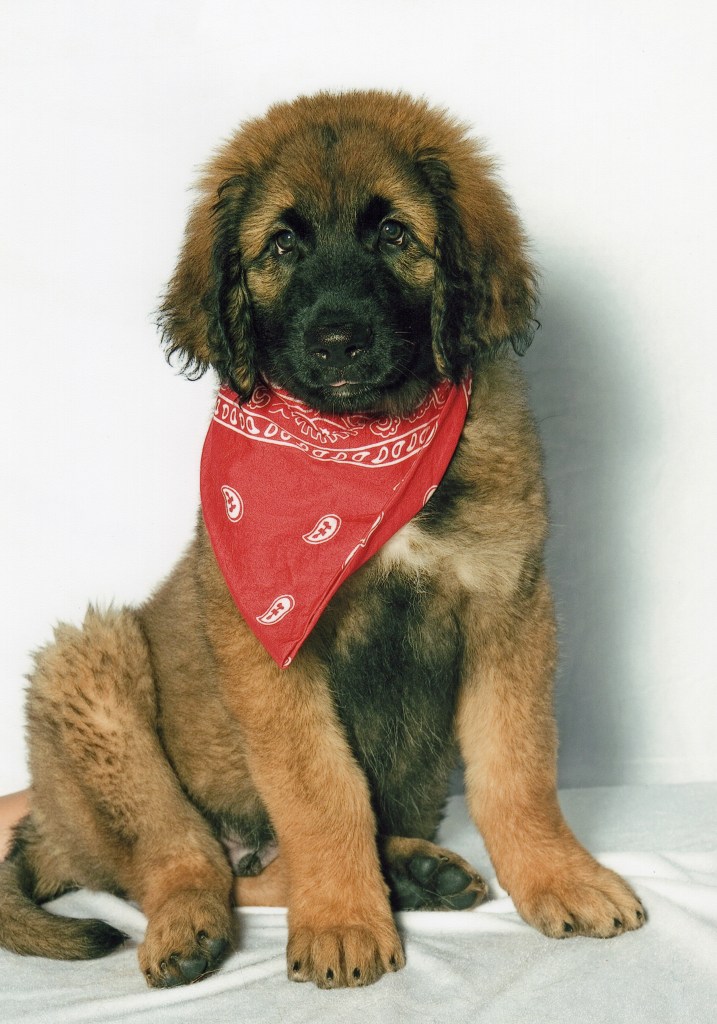
I once apologized to our neighbor Sam because our Leonberger Bronco had been barking. To my surprise Sam told me not to worry, let him bark he said, it scares the bad guys away, and is good for the entire neighborhood. I think the story below, which is an excerpt from my book might explain his thinking.

A quiet and spooky evening alone
It was a quiet evening, and I was home alone. My wife, Claudia, was visiting her parents a few blocks away with Rachel, our daughter. Our son Jacob was meeting with his debate team; our other son, David, was visiting a friend.
I was making myself a ham sandwich in the kitchen when I suddenly felt a hand on my right shoulder. I startled and turned my head to face what I feared was an intruder, and there he stood on his hind legs—our Leonberger, Bronco. His big paw on my shoulder felt for a moment exactly like a human hand.
Bronco looked at me with his kind, wise eyes, then he looked at the sandwich. Then he turned his head toward me again and held my gaze. At that moment I understood what he wanted. I cut the sandwich in two and gave him his half.
The night stalker
I should explain that we had a problem with a trespasser at that time, which was the reason I was startled. This trespasser would sit outside our bedroom window at night and make threats and shout obscene comments at Claudia when I was not present. At first, though, we didn’t know where the threats and comments were coming from. I doubted Claudia’s accounts of these incidents, especially because she thought the voice might be coming from within our bedroom, perhaps via an electronic speaker. I thought she was just having nightmares.
Then one night I heard it myself—a voice screaming, “I am going to burn your house down!” Just as Claudia had said, it sounded like it came from within our bedroom, almost as if it were right next to me.
After Claudia and I went through our “Oh, so now you believe me” routine, I started looking under our bed and inside the heating and air-conditioning vents for hidden speakers and/or microphones. It was hard to believe that someone had planted these things in our bedroom, but that seemed to be the case. Then it finally dawned on me. Next to the headboard of our bed, on Claudia’s side, just inches from her pillow, is a window. At night, when the blinds are lowered and the slats are partially open, you can see in, even if we have just a few lights on in the house. But of course under these conditions, you can’t see anything that might be outside.
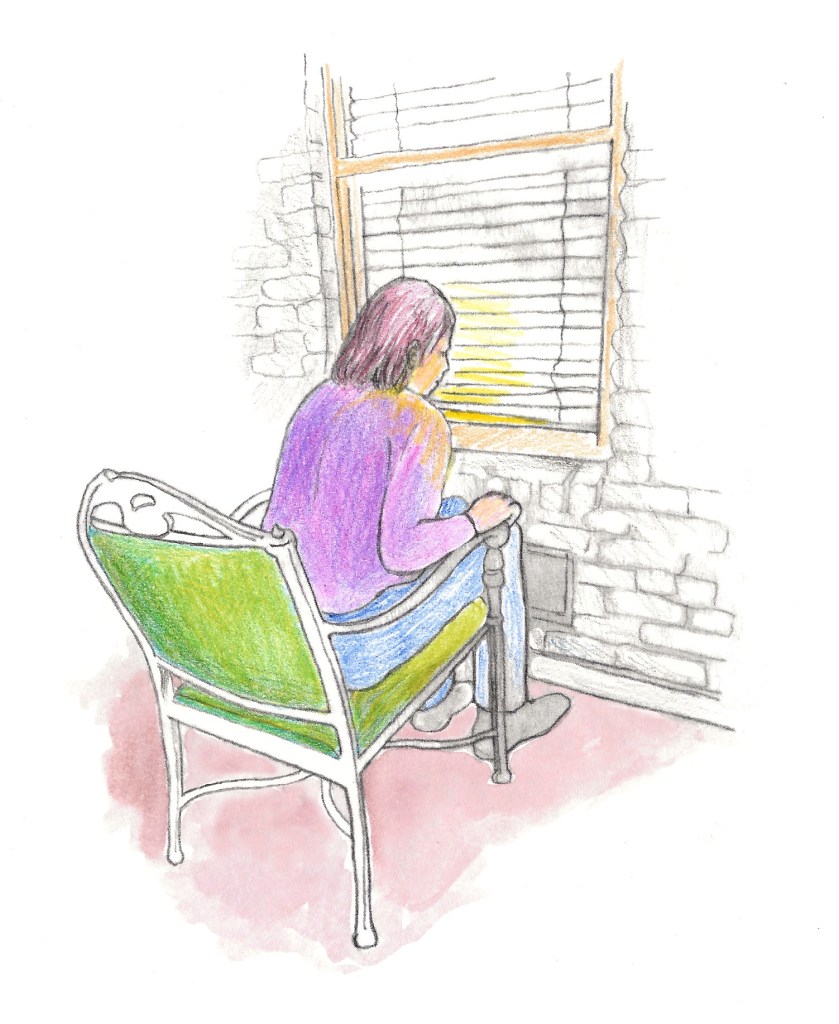

I ran out the front door and around the back of the house, and there, right in front of our bedroom window, was one of our lawn chairs. The trespasser had climbed our fence, taken the chair, sat down in front of the window, and spied on us. Whenever I left the room, he would shout obscenities and threats at Claudia. When his face was planted in front of our window, he was just two or three feet away. This was why the voice felt so close. This had been going on for two weeks. We were happy to have finally figured it out, but we realized we had a problem.
We talked to our neighbors about the situation, and they told us that the trespasser had terrorized them as well. He had been quite busy looking through bedroom windows at night. People in the neighborhood were scared. I called the police, who told us they could do nothing unless the man was caught in the act or he committed a crime other than trespassing.
The detectives
Therefore, I decided to hire private investigators. I found them in the phone book. Phone books still existed back then.
The investigators told me that they typically spy on people suspected of cheating on their spouses, so this would be a more interesting job for them. The plan was for them to hide behind the bushes in our backyard and in a dark car parked on our street. When the man appeared, they would record him on video. They had a lot of fancy equipment and instruments, including big microphones, cameras, and metal detectors. They reminded us of Ghostbusters with all their technology and enthusiasm. They clearly loved their job. Unfortunately, though, the trespasser didn’t show up, so after a couple of days I decided to let the investigators go.
However, I soon figured out who the trespasser was. I started paying attention to what was going on in the neighborhood, and one evening, I noticed a strange-looking but relatively young man, apparently homeless, who seemed to be stealthily roaming our neighborhood. I did not confront him, because I had no proof.
Bronco saves the neighborhood.
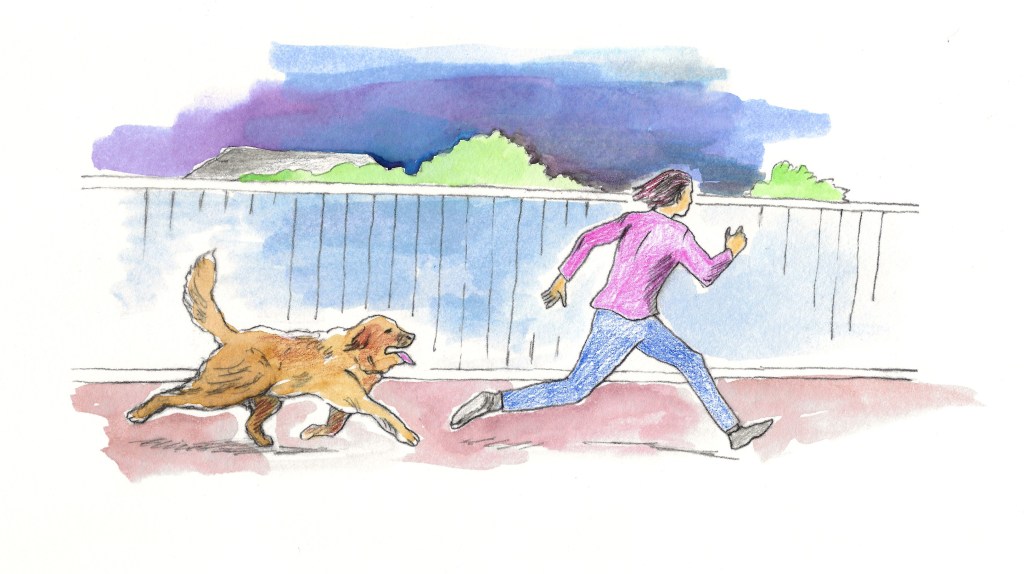
But a few days later, I heard shuffling noises outside our bedroom window. The trespasser was finally back. This time I sent Bronco out to chase him, and he did. Like the detectives, Bronco was enthusiastic but didn’t catch him. Still, he chased the man off. Having a big bearlike dog rushing toward you at night is probably a bit unnerving, even if the dog just wants to lick you. We never experienced or heard about the problem after this event, so Bronco may have helped the entire neighborhood.
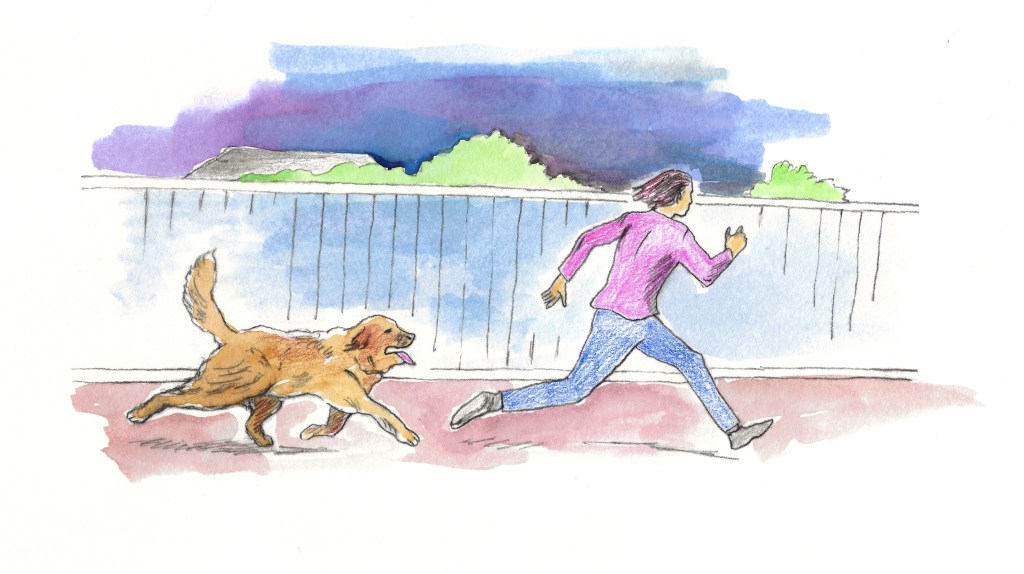

A couple of weeks later, while walking Bronco on a neighboring block, I saw the homeless man across the street, at a bit of a distance. He stared at us in fright. Bronco just calmly looked at him without barking. The man was clearly terrified of Bronco, and he ran away. But despite the nightmare the homeless man had inflicted on us, I felt sorry for him. My guess is that he was suffering from mental illness and that he had had a very tough and lonely life.

Did your dog(s) or pets do something heroic?